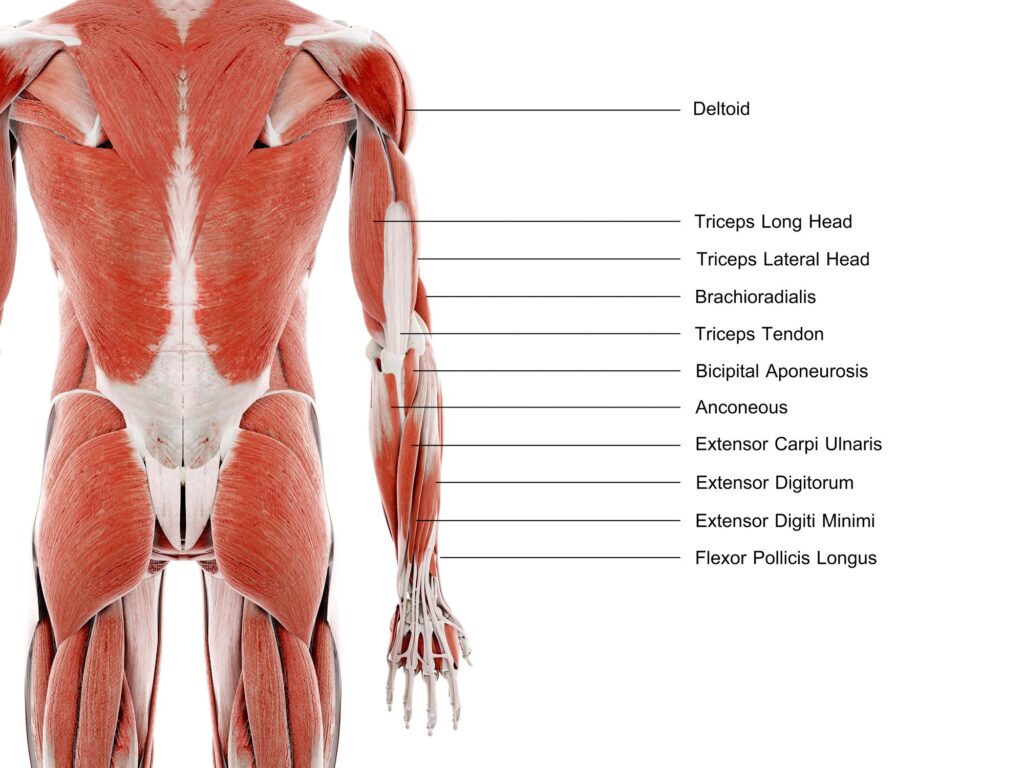
The triceps brachii, often referred to simply as the triceps, is a critical muscle group located on the back of the upper arm. While often overshadowed by its bicep counterpart, the triceps play a vital role in various upper body movements and are essential for strength, stability, and aesthetics. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of the tricep muscles, exploring their anatomy, function, and optimal training strategies.
Anatomy of the Triceps:
The triceps brachii is comprised of three heads: the long head, lateral head, and medial head. These heads originate from different points on the scapula and humerus bone and converge to form a single tendon that inserts into the ulna bone of the forearm. Each head plays a unique role in shoulder and elbow movement:
- Long Head: Originating from the scapula’s infraglenoid tubercle, the long head of the triceps extends down the back of the arm, contributing to shoulder extension and stabilization.
- Lateral Head: This head arises from the posterior surface of the humerus, providing power and stability during elbow extension.
- Medial Head: Originating from the humerus, just below the radial groove, the medial head aids in elbow extension and contributes to overall triceps mass.
Function of the Triceps:
The primary function of the triceps brachii is elbow extension, which involves straightening the arm at the elbow joint. This action is crucial for various activities such as pushing, lifting, and throwing. Additionally, the long head of the triceps assists in shoulder extension, particularly when the arm is raised overhead. Proper development and strength of the triceps are essential for athletic performance, functional movement, and overall upper body aesthetics.
Training Strategies for Triceps Development:
To maximize triceps development, a well-rounded training approach is necessary. Here are some effective strategies:
- Compound Exercises: Incorporate compound movements such as bench presses, overhead presses, and dips, which engage the triceps along with other upper body muscles.
- Isolation Exercises: Include isolation exercises like tricep extensions, skull crushers, and cable pushdowns to target the triceps directly and stimulate muscle growth.
- Progressive Overload: Gradually increase the resistance or weight lifted over time to continually challenge the triceps and promote muscle hypertrophy.
- Variation: Rotate through different exercises, grips, and angles to ensure comprehensive development of all three triceps heads.
- Proper Form: Focus on executing exercises with proper form to effectively target the triceps while minimizing the risk of injury.
Conclusion:
The triceps brachii is a multifaceted muscle group with distinct anatomical features and functional roles. Understanding its anatomy and function is crucial for designing effective training programs aimed at maximizing strength, size, and performance. By incorporating a combination of compound movements, isolation exercises, progressive overload, variation, and proper form, individuals can unlock the full potential of their triceps, leading to improved upper body strength, aesthetics, and functional capacity.





